When to Plant Rose of Sharon Seeds
Rose of Sharon Propagation Methods
When to plant rose of sharon seeds – Propagating Rose of Sharon, also known as Hibiscus syriacus, can be achieved through several methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for successful cultivation.
Seed Starting
Starting Rose of Sharon from seeds offers a potentially cost-effective way to increase the number of plants. However, it’s important to note that seed germination can be unpredictable, and the resulting plants may not always exhibit the same characteristics as the parent plant. Seedlings also require more time to mature compared to plants propagated through other methods.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, potential for large numbers of plants.
- Disadvantages: Low germination rate, slow growth, variable plant characteristics.
Cuttings
Propagating Rose of Sharon via cuttings involves taking stem cuttings from a healthy plant and rooting them to create new plants. This method generally offers a higher success rate and faster maturation than seed starting, and the resulting plants will be genetically identical to the parent plant. However, it requires more hands-on effort and skill.
- Advantages: High success rate, faster maturation, genetically identical plants.
- Disadvantages: Requires more skill and effort, limited number of plants from a single parent.
Layering
Layering involves bending a stem of the existing plant to the ground, burying a portion of it, and encouraging root development before separating it from the parent plant. This method is relatively simple and generally provides a high success rate, but it’s limited by the number of stems suitable for layering on the parent plant. It also takes longer than cuttings.
- Advantages: High success rate, relatively simple, minimal stress on the parent plant.
- Disadvantages: Limited number of plants, slower than cuttings.
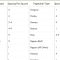
Propagation Method Comparison
| Method | Success Rate | Time to Maturity | Ease of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Starting | Low (20-40%) | 3-5 years | Easy |
| Cuttings | High (70-90%) | 1-2 years | Moderate |
| Layering | High (80-90%) | 2-3 years | Easy |
Ideal Conditions for Rose of Sharon Seed Germination

Source: gardeningknowhow.com
Successful germination of Rose of Sharon seeds depends heavily on providing the optimal environment. This includes careful attention to temperature, soil, moisture, and light.
Optimal Germination Temperature
The ideal temperature range for Rose of Sharon seed germination is between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Temperatures outside this range can significantly reduce germination rates or even prevent germination altogether.
Ideal Soil and Moisture
Well-draining soil is essential for Rose of Sharon seed germination. A seed starting mix that retains some moisture but doesn’t become waterlogged is ideal. Consistent moisture is crucial, but overwatering can lead to fungal diseases. The soil should be kept moist but not soggy.
Light Exposure
While seeds don’t require direct sunlight during germination, providing bright, indirect light is beneficial. Direct sunlight can overheat the seeds and soil, hindering germination.
Preparing Seed Starting Mix and Containers
A well-draining seed starting mix, such as a blend of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite, is recommended. Containers should have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Sterilizing the containers and soil mix beforehand helps prevent fungal diseases.
Sowing Rose of Sharon Seeds: A Step-by-Step Guide

Source: gardeningknowhow.com
Sowing Rose of Sharon seeds requires careful attention to detail to maximize germination rates. Pre-treating the seeds can significantly improve their chances of success.
Step-by-Step Seed Sowing
- Seed Preparation: Scarification (slightly nicking the seed coat) or stratification (cold treatment) may be beneficial to improve germination rates. Soak seeds in warm water for 24 hours before sowing.
- Planting: Sow seeds about ¼ inch deep in a well-draining seed starting mix. Space seeds appropriately to allow for growth.
- Watering: Gently water the seeds after sowing, ensuring the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Light: Place the containers in a location with bright, indirect light.
- Temperature: Maintain a consistent temperature of 65-75°F (18-24°C).
- Germination: Germination typically takes 2-4 weeks.
Visual Representation of Seed Starting Process
Imagine a small container with drainage holes, filled with a moist, dark brown seed-starting mix. Tiny Rose of Sharon seeds are sown about ¼ inch deep, spaced evenly across the surface. The container is then placed in a bright, but not directly sunny, location. After a few weeks, small green shoots emerge from the soil, indicating successful germination.
Timing Considerations for Planting Rose of Sharon Seeds Outdoors
The best time to sow Rose of Sharon seeds outdoors depends heavily on your region’s climate. It’s crucial to avoid frost and freezing temperatures, which can damage or kill young seedlings.
Timing by Climate Zone
- USDA Hardiness Zones 7-10: Direct sowing outdoors can be attempted in late spring after the last frost, typically April-May. Starting seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last frost is recommended for earlier blooms.
- USDA Hardiness Zones 5-6: Starting seeds indoors 8-10 weeks before the last frost is highly recommended. Direct sowing outdoors is generally risky due to potential frost damage.
- USDA Hardiness Zones below 5: Starting seeds indoors is essential, with transplanting to the garden only after all danger of frost has passed.
Indoors vs. Outdoors
- Indoors: Offers greater control over environmental conditions, leading to higher germination rates and earlier blooms. Requires more effort and resources.
- Outdoors: Simpler, less resource-intensive, but subject to environmental variables, leading to lower germination rates and potential for damage.
Post-Germination Care for Rose of Sharon Seedlings: When To Plant Rose Of Sharon Seeds
Once Rose of Sharon seeds germinate, providing adequate care is vital for healthy seedling development. This includes consistent watering, fertilization, and monitoring for diseases.
Sunlight, Water, and Nutrients
Seedlings need ample sunlight (at least 6 hours daily), consistent moisture, and regular fertilization. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to damping-off disease. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Common Seedling Problems
- Damping-off: A fungal disease that causes seedlings to rot at the base. Prevent it by using sterile soil and containers and avoiding overwatering.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Yellowing leaves or stunted growth can indicate nutrient deficiencies. Use a balanced fertilizer to address this.
Watering and Fertilization Schedule
| Week | Watering | Fertilization | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | Keep soil consistently moist | None | Monitor for damping-off |
| 5-8 | Water when top inch of soil is dry | Diluted balanced fertilizer every 2 weeks | Increase sunlight exposure gradually |
| 9 onwards | Water as needed, allowing soil to dry slightly between waterings | Diluted balanced fertilizer every week | Monitor growth and adjust watering/fertilization accordingly |
Transplanting Rose of Sharon Seedlings
Transplanting Rose of Sharon seedlings requires careful handling to minimize stress and ensure survival. Choosing the right location and preparing the planting site are crucial steps.
Transplanting Process
- Choosing Location: Select a location with at least 6 hours of sunlight per day and well-draining soil.
- Site Preparation: Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and fertility. Remove weeds and rocks from the planting area.
- Transplanting: Gently remove seedlings from their containers, avoiding root damage. Plant seedlings at the same depth they were growing in their containers, spacing them appropriately (2-4 feet apart).
- Watering: Water thoroughly after transplanting to settle the soil around the roots.
Planting Location and Spacing, When to plant rose of sharon seeds
Rose of Sharon thrives in full sun to partial shade. Proper spacing is crucial to allow for adequate air circulation and prevent overcrowding. A spacing of 2-4 feet between plants is generally recommended.
Helpful Answers
Can I start Rose of Sharon seeds directly outdoors?
While possible in warmer climates, starting seeds indoors is generally recommended for better germination rates and protection from frost.
How long does it take for Rose of Sharon seeds to germinate?
Germination can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on conditions and seed viability.
Rose of Sharon seeds, ideally sown indoors in late winter, benefit from a warm start. Timing is crucial for successful germination, much like the optimal time for planting other seeds, such as knowing when to plant grass seed in Pennsylvania in spring, which you can find out more about here: when to plant grass seed pennsylvania spring.
After the last frost, you can transplant your rose of Sharon seedlings outdoors, ensuring they have sufficient sunlight and well-drained soil.
What should I do if my Rose of Sharon seedlings look leggy?
Leggy seedlings indicate insufficient light; increase light exposure or use grow lights.
My Rose of Sharon seedlings have damped off; what can I do?
Damped-off is a fungal disease; improve air circulation, use sterile seed starting mix, and consider a fungicide.