When to Plant Sunflower Seeds in Michigan
Ideal Planting Time in Michigan
When to plant sunflower seeds in michigan – Determining the optimal time to plant sunflowers in Michigan requires considering the state’s diverse microclimates and the specific sunflower variety. Factors like the last frost date, soil temperature, and the desired harvest time all play a crucial role. Generally, planting occurs after the danger of frost has passed, typically between late May and early June, but variations exist across different regions.
Optimal Planting Timeframe and Regional Variations
The ideal planting timeframe for sunflowers in Michigan stretches from late May to early June for most areas. However, northern Michigan experiences a later last frost date, pushing planting closer to early June or even mid-June. Southern Michigan, benefiting from warmer temperatures, may allow for planting as early as late May. This variance necessitates a region-specific approach.
| Region | Early Planting Date | Optimal Planting Date | Late Planting Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southern Michigan | May 20th | May 25th – June 5th | June 10th |
| Central Michigan | May 25th | June 5th – June 15th | June 20th |
| Northern Michigan | June 5th | June 10th – June 20th | June 25th |
Factors like soil temperature are equally important. The soil should be consistently above 50°F (10°C) for optimal germination. Monitoring weather forecasts and soil temperatures using a soil thermometer is highly recommended before planting.
Planting Times for Different Sunflower Varieties
| Variety | Days to Maturity | Southern Michigan Planting | Northern Michigan Planting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Season (e.g., ‘Sonja’) | 50-60 days | May 20th – May 30th | June 5th – June 15th |
| Mid-Season (e.g., ‘Mammoth’) | 70-80 days | May 25th – June 5th | June 10th – June 20th |
| Late Season (e.g., ‘Russian Mammoth’) | 90-100 days | June 1st – June 10th | June 15th – June 25th |
Soil Preparation and Site Selection
Successful sunflower cultivation hinges on proper soil preparation and site selection. Sunflowers thrive in well-drained, fertile soil rich in organic matter. Choosing a location with ample sunlight is crucial for robust growth.
Soil Conditions and Preparation
Sunflowers prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.5. Before planting, conduct a soil test to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and fertility. This enhances water retention and provides essential nutrients. Till the soil to a depth of 12-18 inches to create a loose, workable planting bed.
Ideal Site Selection
Sunflowers require at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight daily. Select a location with minimal shade. Ensure the site has excellent drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. Avoid areas prone to strong winds, which can damage tall sunflower plants.
Step-by-Step Site Preparation Guide
A detailed step-by-step guide would involve: 1. Soil testing to determine pH and nutrient levels; 2. Soil amendment with compost or other organic matter; 3. Tilling the soil to a depth of 12-18 inches; 4. Selecting a sunny location with good drainage; 5.
Removing weeds and rocks from the planting area; 6. Creating raised beds if necessary for better drainage; 7. Watering the soil thoroughly before planting. Imagine a diagram showing these steps, with each step clearly illustrated with detailed descriptions of the process and tools involved.
Seed Selection and Planting Methods
Choosing the right sunflower seeds and employing the appropriate planting method are vital for successful cultivation. Various sunflower types cater to different preferences, from dwarf varieties suitable for smaller gardens to giant sunflowers for impressive displays. Direct sowing is common in Michigan’s climate, but starting seeds indoors offers an advantage in shorter growing seasons.
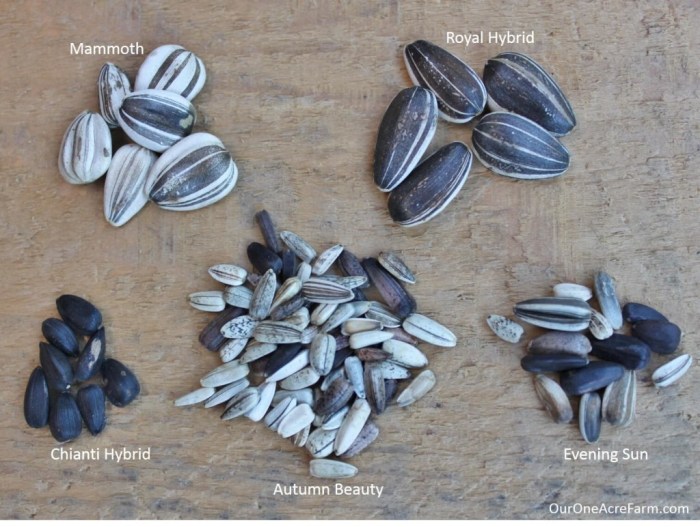
Sunflower Seed Types
Michigan gardeners have a wide selection: dwarf sunflowers (reaching heights of 1-3 feet), perfect for containers or smaller gardens; giant sunflowers (growing up to 10-15 feet tall), ideal for dramatic displays; and ornamental sunflowers, prized for their unique flower shapes and colors. Choosing the right type depends on available space and desired aesthetic.
Direct Sowing vs. Starting Indoors

Source: ouroneacrefarm.com
Direct sowing is generally preferred in Michigan due to the relatively short growing season. However, starting seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost date allows for an earlier harvest, especially for late-season varieties. This approach requires careful management of temperature and light to prevent leggy seedlings.
Planting Sunflower Seeds Directly into the Ground
Plant seeds 1-2 inches deep and 6-12 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water gently after planting. Keep the soil consistently moist until germination. Thin seedlings to the desired spacing once they reach a few inches tall to allow for optimal growth.
Tips for Successful Seed Germination and Seedling Establishment
- Choose high-quality seeds from a reputable source.
- Plant seeds at the correct depth and spacing.
- Maintain consistent soil moisture.
- Protect seedlings from pests and diseases.
- Thin seedlings to prevent overcrowding.
Sunflower Care and Maintenance
Providing adequate care and maintenance ensures healthy sunflower growth and a bountiful harvest. This includes addressing potential pest and disease issues, implementing appropriate watering and fertilization strategies, and supporting tall plants to prevent breakage.
In Michigan, the ideal time to plant sunflower seeds is after the last frost, typically around late May or early June. Determining the best planting time often involves considering other similar plants; for instance, you might also want to check out this guide on when to plant nigella seeds , as similar soil and weather conditions apply. Successfully germinating sunflower seeds hinges on warm soil temperatures, much like other cool-season annuals.
Pest and Disease Management
Common sunflower pests in Michigan include birds, squirrels, aphids, and caterpillars. Preventative measures include using row covers to protect seedlings from birds and using insecticidal soap or neem oil to control insect infestations. Diseases like downy mildew and rust can be managed by ensuring good air circulation and avoiding overhead watering. Rotating crops can also help prevent disease build-up.
Watering and Fertilization
Sunflowers require consistent watering, especially during dry spells. Aim for 1-2 inches of water per week. Fertilize with a balanced fertilizer according to package directions. Over-fertilizing can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of flower production.
Supporting Tall Sunflower Plants
Tall sunflower varieties may require staking or other support to prevent them from breaking in strong winds or under the weight of their heavy flower heads. Use sturdy stakes and ties to provide support.
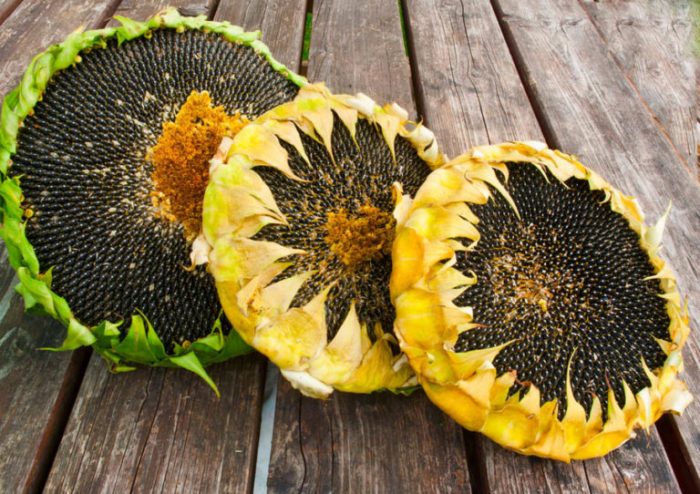
Harvesting Sunflower Seeds
Harvest sunflower seeds when the back of the flower head turns brown and the seeds are plump and dry. Cut the flower heads and allow them to dry completely in a cool, dry place. Once dry, remove the seeds and store them in an airtight container.
Dealing with Michigan’s Climate Challenges: When To Plant Sunflower Seeds In Michigan

Source: shuncy.com
Michigan’s climate presents certain challenges for sunflower growers. Late spring frosts, drought conditions, and excessive rainfall can all impact sunflower growth and yield. Understanding these challenges and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is essential for success.
Protecting Seedlings from Late Spring Frosts
Cover seedlings with row covers or other frost protection materials if a late frost is predicted. This protects young plants from damage and ensures successful establishment.
Managing Drought Conditions
During dry periods, provide supplemental irrigation to maintain consistent soil moisture. Mulching around plants helps retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
Handling Excessive Rainfall or Humidity

Source: gardenzeus.com
Excessive rainfall can lead to waterlogging and fungal diseases. Ensure good drainage and avoid overhead watering. Consider using fungicides if necessary to prevent fungal diseases.
Resources for Michigan Gardeners, When to plant sunflower seeds in michigan
- Michigan State University Extension
- Local garden centers and nurseries
- Online gardening forums and communities
Helpful Answers
What are the best sunflower varieties for Michigan?
Several varieties thrive in Michigan’s climate. Choose shorter varieties for areas with higher winds, and consider disease-resistant options for better success.
How deep should I plant sunflower seeds?
Plant sunflower seeds about 1 inch deep and space them 6-12 inches apart.
What should I do if my sunflowers get too tall and start to lean?
Stake taller varieties to prevent them from breaking in strong winds. You can use sturdy stakes and tie the plants gently.
When can I harvest my sunflower seeds?
Harvest when the back of the flower head turns brown and the seeds are plump and dry. You can also test seed ripeness by gently rubbing a seed between your fingers; if it easily separates from the head, it’s ready.