When to Plant Zinnia Seeds in Georgia
Understanding Georgia’s Climate and Zinnia Planting
When to plant zinnia seeds in georgia – Georgia’s diverse geography results in varying climates across the state, significantly impacting the optimal planting times for zinnias. Understanding your specific USDA Plant Hardiness Zone is crucial for successful zinnia cultivation. This involves knowing your area’s average last and first frost dates, which determine when the risk of frost damage is minimal.
Georgia’s USDA Plant Hardiness Zones and Frost Dates
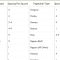
Georgia encompasses USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 7a through 8b. These zones indicate the average annual minimum winter temperatures. The last frost date and first frost date vary within these zones, influencing the ideal time to plant zinnias. Later planting in colder zones is necessary to avoid frost damage. Earlier planting in warmer zones allows for a longer blooming season.
| Zone | Last Frost Date (Approximate) | First Frost Date (Approximate) | Optimal Zinnia Planting Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | Mid-April | Late October | Late April – Early May |
| 7b | Early April | Mid-November | Late March – April |
| 8a | Late March | Early November | Mid-March – April |
| 8b | Mid-March | Late November | Early March – April |
Note: These are approximate dates. Consult local weather forecasts for the most accurate predictions.
Direct Sowing Zinnia Seeds Outdoors
Direct sowing zinnia seeds outdoors is a simple and effective method, especially in Georgia’s warmer zones. This involves planting the seeds directly into the garden bed, eliminating the need for transplanting. Proper soil preparation and seed placement are crucial for successful germination and growth.
Direct Sowing Guide, When to plant zinnia seeds in georgia
- Prepare the soil: Loosen the soil to a depth of about 12 inches, ensuring good drainage. Amend the soil with compost to improve fertility and drainage. Zinnias thrive in well-drained soil.
- Choose a sunny location: Zinnias require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Plant the seeds: Sow seeds about ¼ inch deep and 1 inch apart. Thinner seedlings can be transplanted later.
- Water gently: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged until germination.
- Thin seedlings: Once seedlings emerge, thin them to 6-12 inches apart, depending on the variety.
Ideal soil temperature for zinnia germination is between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Proper seed spacing ensures sufficient space for each plant to grow and minimizes competition for resources.
Starting Zinnia Seeds Indoors
Starting zinnias indoors provides a head start, especially in cooler zones or for an extended blooming season. This allows for earlier flowering and potentially a more robust plant. Careful planning and execution are needed to avoid common pitfalls.
Indoor Starting Schedule
To determine the ideal starting time, subtract 6-8 weeks from your area’s last frost date. This allows sufficient time for seedlings to mature before transplanting outdoors.
Container and Potting Mix Requirements
Use seed-starting trays or individual pots with drainage holes. A well-draining seed-starting mix is essential to prevent damping-off (a fungal disease).
Transplanting Seedlings
Once the last frost has passed and seedlings have developed several true leaves, gradually harden them off by placing them outdoors for increasing periods each day before transplanting into the garden.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
- Damping-off: Overwatering and poor drainage can cause this fungal disease. Use well-draining mix and avoid overwatering.
- Leggy seedlings: Insufficient light can lead to weak, leggy seedlings. Provide supplemental lighting if necessary.
- Rootbound seedlings: Overcrowding can restrict root growth. Use appropriately sized containers and thin seedlings as needed.
Zinnia Varieties and Planting Needs: When To Plant Zinnia Seeds In Georgia
Numerous zinnia varieties are available, each with unique characteristics affecting their planting requirements. Choosing the right variety for your location and desired aesthetic is crucial for success. Factors like plant height, bloom time, and overall growth habit should be considered.
Zinnia Variety Comparison
| Variety | Planting Time | Height | Bloom Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| California Giant | Late spring | Tall (36 inches) | Summer-fall |
| Profusion | Spring | Dwarf (12-18 inches) | Summer-fall |
| Envy | Spring | Medium (24 inches) | Summer-fall |
Dwarf zinnias are ideal for smaller spaces, borders, or containers, while tall varieties make striking additions to flowerbeds or as cut flowers. Selecting a variety depends on the available space, desired height, and personal preference.
Factors Affecting Zinnia Growth in Georgia
Several environmental factors significantly influence zinnia growth and flowering in Georgia. Understanding these factors and providing optimal conditions is essential for healthy, vibrant plants. Proper sunlight, soil conditions, and pest management are crucial.
Sunlight, Soil, and Pests

Source: thespruce.com
Zinnias need at least six hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal flowering. Well-drained soil prevents root rot and ensures healthy growth. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and slugs. Regular monitoring and appropriate pest control measures, such as insecticidal soap or neem oil, are crucial.
Ideal Growing Conditions
Imagine a vibrant illustration: A sunny location with rich, well-drained soil, plants spaced appropriately for air circulation, and regular watering. This visualization represents the ideal environment for zinnia cultivation in Georgia. The illustration would show healthy zinnias with abundant blooms, thriving in a well-maintained garden setting.
Maintaining Zinnia Plants

Source: thespruce.com
Proper maintenance ensures continuous blooming and healthy growth throughout the season. Consistent watering, fertilization, and deadheading are key practices for maximizing zinnia performance in Georgia’s climate.
Watering, Fertilizing, and Deadheading
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry spells. A balanced fertilizer applied every 2-3 weeks promotes abundant blooms. Deadheading (removing spent flowers) encourages continuous flowering and prevents seed production, which can prematurely end the blooming cycle. Removing spent flowers also improves the overall look of the plant.
To extend the blooming season, consider planting successive crops or using succession planting techniques. This involves planting additional seeds at intervals to ensure a continuous display of blooms throughout the growing season. This helps ensure continuous blooms from early summer through to late fall.
For optimal Zinnia growth in Georgia, aim for a frost-free period, typically after the last frost in spring. This timing aligns with many other warm-season annuals. Determining the ideal planting time often involves considering similar climates; for instance, understanding when to plant other flowers, such as the information provided on when to plant poppy seeds in California , can offer helpful comparisons.
Ultimately, successful Zinnia cultivation hinges on consistent warmth and sufficient sunlight in Georgia.
Helpful Answers
What type of soil is best for zinnias in Georgia?
Zinnias thrive in well-drained, fertile soil. Amend heavy clay soils with compost to improve drainage.
How often should I water my zinnias?
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry spells, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Can I save zinnia seeds from my plants?
Yes, allow some flowers to go to seed, then collect and store the seeds in a cool, dry place for planting the following year.
What are some common zinnia pests in Georgia?
Watch out for aphids, spider mites, and slugs. Use insecticidal soap or other appropriate pest control methods as needed.