Can I Plant Pumpkin Seeds?
Planting Pumpkin Seeds: A Comprehensive Guide: Can I Plant Pumpkin Seeds
Source: wikihow.com
Can i plant pumpkin seeds – Growing pumpkins can be a rewarding experience, yielding delicious fruits for culinary use and festive decorations. Success hinges on understanding the ideal timing, soil conditions, and cultivation techniques. This guide provides a detailed overview of planting pumpkin seeds, from seed selection to harvesting and storage.
Ideal Timing and Planting Conditions

Source: hearstapps.com
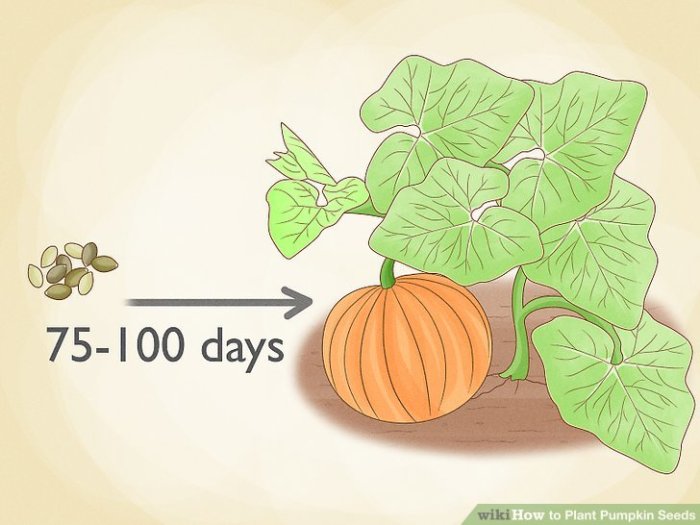
The ideal time to plant pumpkin seeds depends heavily on your climate and USDA hardiness zone. Pumpkins require warm soil and ample sunlight to thrive. Early planting in cooler zones risks frost damage, while late planting may result in insufficient time for maturation before the first frost.
| Zone | Planting Date (Early) | Planting Date (Late) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-4 | May 15-June 1 | June 15-July 1 | Start seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last expected frost. |
| 5-6 | May 1-May 15 | May 15-June 1 | Direct sowing may be possible in warmer areas. |
| 7-8 | April 15-May 1 | May 15-June 15 | Warmer temperatures allow for earlier planting. |
| 9-10 | April 1-April 15 | May 1-May 15 | Consider multiple plantings for extended harvest. |
Pumpkin seeds need well-drained, fertile soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0-7.0). Poor drainage can lead to root rot. Improving soil structure is crucial for optimal growth.
- Adding compost improves soil fertility and drainage.
- Incorporating aged manure adds organic matter and nutrients.
- Amend heavy clay soils with perlite or vermiculite to improve aeration.
- Sandy soils benefit from the addition of peat moss to increase water retention.
Pumpkins thrive in full sun (at least 6-8 hours daily) and warm temperatures (ideally 70-80°F). An ideal pumpkin patch is a sunny location with well-drained soil, protected from strong winds. Visualize a sunny field with rows of healthy, green plants, basking in the warmth, with loose, dark soil around their bases.
Pumpkin Seed Starting Methods: Direct Sowing vs. Indoor Starting
Two primary methods exist for starting pumpkin seeds: direct sowing outdoors and starting seeds indoors. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Yes, you can certainly plant pumpkin seeds! Timing is key for a successful harvest, and understanding the optimal planting window is crucial. Similar considerations apply to other plants like sunflowers; for guidance on that, check out this helpful resource on when to plant sunflower seed. Knowing the best time to plant sunflowers helps you better understand the general principles applicable to planting pumpkin seeds as well, ensuring a bountiful yield for both.
| Method | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Advantages: Simpler process, avoids transplant shock. Disadvantages: Slower germination, higher risk of seed loss due to pests or weather. |
| Indoor Starting | Advantages: Earlier harvest, higher germination rates, better control over environmental conditions. Disadvantages: Requires more effort, potential for transplant shock if not done carefully. |
Starting Pumpkin Seeds Indoors: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting seeds indoors provides a head start, increasing the chances of a successful harvest, especially in shorter growing seasons. Follow these steps for optimal results:
- Choose Containers: Select small pots (2-3 inches in diameter) with drainage holes. Imagine sturdy, peat pots that are easy to handle and won’t damage the roots during transplanting.
- Potting Mix: Use a seed-starting mix that’s light, airy, and well-draining. Picture a rich, dark brown mix that’s free of large clumps.
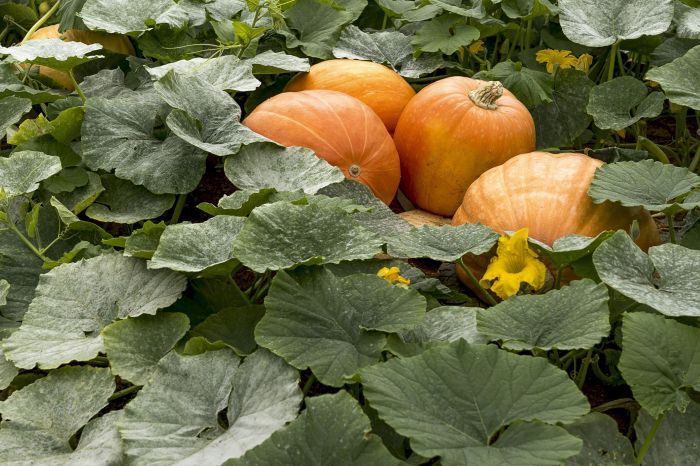
- Planting: Sow one seed per pot, about 1 inch deep. Gently cover with soil and lightly water. Imagine a delicate process, ensuring the seed is properly covered but not buried too deeply.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Visualize a watering can with a gentle rose, ensuring even moisture without overwatering.
- Light and Temperature: Provide ample sunlight (at least 6 hours daily) and a warm temperature (70-80°F). Imagine a sunny windowsill or a grow light setup.
- Hardening Off: Gradually acclimate seedlings to outdoor conditions before transplanting. Picture gradually increasing exposure to sunlight and wind over a week.
Direct Sowing Pumpkin Seeds Outdoors
Direct sowing is a simpler method suitable for warmer climates. Prepare the soil by loosening it and removing any weeds or rocks. Plant seeds 1 inch deep and 4-6 feet apart. Gently firm the soil around the seeds. Water thoroughly after planting.
This method allows the roots to grow directly into the prepared soil, reducing the risk of transplant shock.
Pumpkin Seed Selection and Care
Choosing the right pumpkin variety is essential for a successful harvest. Different varieties have varying sizes, growing times, and climate preferences.
| Variety | Size | Growing Time (days) | Climate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connecticut Field | Large | 100-110 | Cool to warm |
| Howden Biggie | Giant | 110-120 | Warm |
| Jack O’Lantern | Medium | 90-100 | Warm |
| Baby Boo | Small | 85-95 | Warm |
Several issues can affect pumpkin growth. Addressing these problems promptly is crucial for maximizing yield.
- Damping-off: A fungal disease that causes seedlings to rot at the base. Preventative measures include using sterile soil and avoiding overwatering. Solutions include applying a fungicide.
- Pest Infestations: Squash bugs, vine borers, and aphids can damage pumpkin plants. Regular inspection, handpicking pests, and using insecticidal soap are effective control measures.
To ensure a bountiful harvest, consistent care is essential.
- Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer according to package instructions.
- Monitor for pests and diseases, taking prompt action if necessary.
- Provide support for vines as they grow to prevent damage.
Pumpkin Harvesting and Storage, Can i plant pumpkin seeds

Source: minnetonkaorchards.com
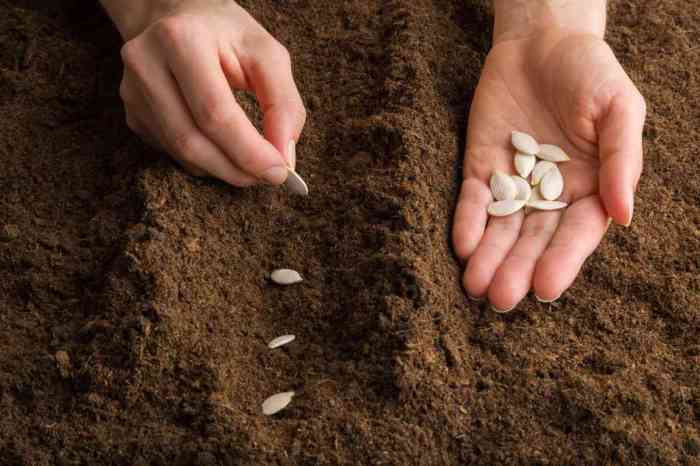
Knowing when and how to harvest pumpkins is key to preserving their quality and extending their shelf life. A ripe pumpkin will have a deep orange color, a hard rind that resists indentation, and a dry stem.
Visualize a pumpkin with a rich, deep orange hue, a hard, woody stem, and a solid feel when tapped. The rind should be free of blemishes and soft spots.
Harvest pumpkins carefully using a sharp knife or shears, cutting the stem several inches from the fruit. Avoid bruising the pumpkin during harvest. Lift the pumpkin gently to prevent damage.
Proper storage is essential for extending the shelf life of harvested pumpkins.
- Store pumpkins in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Avoid stacking pumpkins directly on top of each other.
- Keep pumpkins away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- For long-term storage, consider curing pumpkins in a cool, dry place for several weeks.
FAQ Overview
How deep should I plant pumpkin seeds?
Plant pumpkin seeds about 1-2 inches deep.
How far apart should I space pumpkin plants?
Spacing depends on the variety, but generally, allow 4-6 feet between plants.
What should I do if my pumpkin seedlings are damping off?
Ensure good air circulation, avoid overwatering, and consider using a fungicide.
How long does it take for pumpkin seeds to germinate?
Germination typically takes 7-10 days, but it can vary depending on conditions.
Can I save pumpkin seeds from my harvest for planting next year?
Yes, but make sure to select seeds from healthy, mature pumpkins and allow them to dry thoroughly before storing.