Pumpkin Seed Viability
Can i plant a pumpkin seed – Successfully growing pumpkins starts with viable seeds. Several factors influence a pumpkin seed’s ability to germinate and grow into a healthy plant. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing your chances of a bountiful harvest.
Factors Affecting Pumpkin Seed Germination
Several factors influence the success of pumpkin seed germination. These include the seed’s age and storage conditions, the quality of the parent plant, and environmental conditions during germination. Older seeds, or those improperly stored (e.g., in damp conditions), are less likely to germinate. Seeds from healthy, vigorous parent plants generally exhibit higher viability.
Optimal Conditions for Pumpkin Seed Sprouting
For optimal sprouting, pumpkin seeds require specific environmental conditions. A soil temperature between 70-90°F (21-32°C) is ideal. Consistent moisture is essential; the soil should be kept evenly moist but not waterlogged. While pumpkin seedlings benefit from sunlight later in their development, they initially germinate best in the dark or low-light conditions.
Viability of Seeds from Different Pumpkin Varieties
The viability of pumpkin seeds can vary slightly depending on the variety. Generally, heirloom varieties, known for their longevity, may show slightly lower germination rates compared to commercially produced hybrid seeds. However, proper storage and handling techniques can mitigate this difference. Seed packets usually provide germination rate information.
Testing Seed Viability Before Planting
A simple test can assess seed viability before planting. Place a few seeds between moist paper towels in a sealed plastic bag. Keep them at room temperature. After a few days, check for signs of germination – a visible sprout emerging from the seed. Seeds that don’t show signs of germination within a week are likely non-viable.
Planting Methods: Can I Plant A Pumpkin Seed
Pumpkin seeds can be planted directly outdoors or started indoors for a head start. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Direct Sowing vs. Starting Indoors
The choice between direct sowing and starting indoors depends on your climate and desired harvest time. Direct sowing is simpler but risks slower growth and potential damage from pests or weather. Starting indoors provides a faster start and better control over conditions, but requires transplanting, which can stress the seedlings.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Simple, less work | Slower growth, susceptible to weather and pests | Warm climates, experienced gardeners |
| Starting Indoors | Faster growth, better control over conditions | Requires transplanting, more effort | Cool climates, short growing seasons |
Seed Depth and Spacing
Planting depth and spacing are crucial for successful pumpkin growth. Seeds should be planted about 1 inch deep. Spacing depends on the variety but generally ranges from 4-6 feet apart for vining pumpkins to allow for ample growth.
Optimal Planting Techniques, Can i plant a pumpkin seed
A visual guide would show: (1) Preparing the soil – loosening and enriching it; (2) Planting seeds – placing seeds at the correct depth and spacing; (3) Covering seeds – lightly covering with soil; (4) Watering – gently watering the soil after planting. The illustration would highlight the importance of proper spacing and depth.
Soil and Environmental Factors
Pumpkins thrive in well-drained, fertile soil. Sunlight, water, and nutrients are essential for healthy growth.
Ideal Soil Type and pH
Pumpkins prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH of 6.0-6.8. Well-drained loam soil is ideal. Sandy soil may require amendment with compost to improve water retention. Clay soils may need amending with organic matter to improve drainage.
Role of Sunlight, Water, and Nutrients
Pumpkins need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Consistent watering is crucial, especially during dry periods. Regular fertilization with a balanced fertilizer supports vigorous growth and fruit production. Nitrogen is particularly important for vine growth, while phosphorus and potassium are essential for fruit development.
Improving Soil Conditions
Improving soil conditions involves amending the soil with compost or other organic matter to enhance drainage, aeration, and nutrient content. Soil testing can determine nutrient deficiencies, allowing for targeted fertilization.
Common Problems and Solutions
Poor soil drainage can lead to root rot. Nutrient deficiencies may result in stunted growth or yellowing leaves. These issues can be addressed by improving soil drainage and using appropriate fertilizers. Lack of sunlight can result in poor fruit production. Providing adequate sunlight is crucial.
| Problem | Description | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Rot | Decaying roots, wilting plants | Poor drainage, overwatering | Improve drainage, adjust watering |
| Nutrient Deficiency | Yellowing leaves, stunted growth | Lack of essential nutrients | Apply balanced fertilizer |
| Poor Fruit Production | Small or few pumpkins | Insufficient sunlight, inadequate pollination | Ensure adequate sunlight, hand-pollinate if necessary |
Post-Planting Care
Consistent care is essential for healthy pumpkin growth and a successful harvest. This includes regular watering, weed control, pest management, and providing support for the vine.
Watering Requirements

Source: gardeningtips.in
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods. Young seedlings require frequent watering, while mature plants need less frequent but deeper watering. Avoid overhead watering to prevent fungal diseases.
Weed Control and Pest Management
Regular weeding prevents competition for nutrients and water. Pest control may involve using organic methods like companion planting or insecticidal soaps to deter pests. Monitoring for pests and diseases is important for early intervention.
Fertilizing Schedule
A balanced fertilizer should be applied at planting and again during the flowering and fruiting stages. Follow the fertilizer instructions carefully, avoiding over-fertilization.
Supporting the Pumpkin Vine
As the vine grows, it may need support to prevent it from sprawling on the ground. Trellises, stakes, or other supports can help keep the vine off the ground, improving air circulation and reducing the risk of rot.
Potential Problems and Solutions

Source: hearstapps.com
Several problems can affect pumpkin growth. Understanding these problems and their solutions is essential for successful pumpkin cultivation.
Yes, you can certainly plant a pumpkin seed; it’s a straightforward process. Timing is key, however, much like deciding when to plant other seeds, such as determining the optimal time for tasks like when to plant grass seed in PA fall. Understanding seasonal changes is vital for successful gardening, whether you’re growing pumpkins or establishing a lush lawn.
Therefore, successful pumpkin cultivation hinges on appropriate timing and conditions, just like grass seed planting.
Common Problems and Solutions
Damping-off is a fungal disease affecting seedlings. Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease affecting leaves and stems. Squash vine borers are destructive pests that tunnel into the vine. These problems can be addressed through preventative measures such as proper soil preparation, adequate spacing, and timely intervention with appropriate fungicides or pest control methods.
| Problem | Description | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damping-off | Seedling wilting and death | Fungal pathogens in wet soil | Use well-draining soil, avoid overwatering, use fungicide |
| Powdery Mildew | White powdery coating on leaves | Fungal infection | Improve air circulation, use fungicide |
| Squash Vine Borers | Wilting vines, holes in stems | Insect larvae | Monitor for borers, use insecticides, handpick larvae |
Harvesting and Storage
Knowing when to harvest and how to store pumpkins properly ensures a long-lasting harvest.
Signs of Pumpkin Ripeness
Pumpkins are ready for harvest when the rind is hard and the stem is dry and woody. The color should be deep and characteristic of the variety. A ripe pumpkin will have a dull sound when thumped.
Harvesting Method
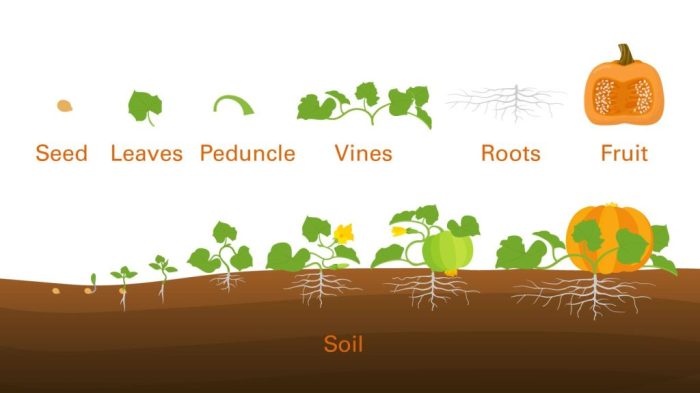
Source: ncsu.edu
Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to cut the pumpkin from the vine, leaving a few inches of stem attached. Handle pumpkins carefully to avoid bruising.
Curing and Storage
Curing involves allowing pumpkins to dry in a cool, dry place for several weeks before storage. Proper curing extends shelf life. Store pumpkins in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
Preserving Pumpkin Seeds
Clean and dry pumpkin seeds thoroughly. Store them in a cool, dry, and airtight container for future planting. Properly stored seeds can retain viability for several years.
Questions and Answers
How long does it take for a pumpkin seed to germinate?
Germination typically takes 7-10 days, but it can vary depending on factors like temperature and seed viability.
Can I save seeds from store-bought pumpkins for planting?
It’s possible, but the resulting pumpkins may not be true to type. Hybrid pumpkins often produce seeds that don’t grow into identical plants.
What should I do if my pumpkin seedlings are leggy?
Leggy seedlings indicate insufficient light. Move them closer to a light source or increase the light intensity.
How often should I water my pumpkin plants?
Water deeply and regularly, especially during dry spells, aiming for consistently moist but not soggy soil.



