Health Benefits and Potential Drawbacks
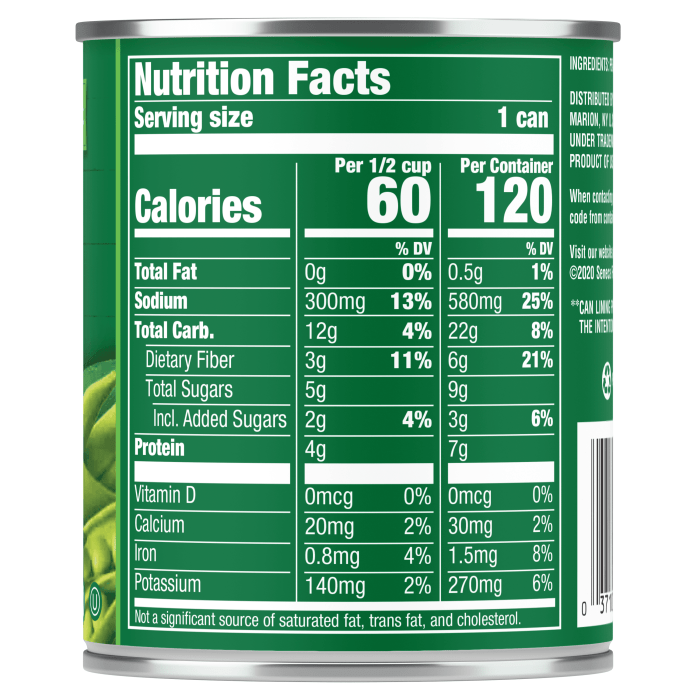
Canned green peas nutrition facts – Canned green peas, while a convenient and readily available source of nutrients, present a mixed bag when considering their impact on health. Understanding both their benefits and potential drawbacks is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will explore the advantages and disadvantages of incorporating canned green peas into your diet, considering factors like fiber content, sodium levels, and their effects on specific health conditions.
The nutritional profile of canned green peas offers several compelling reasons for their inclusion in a balanced diet. Their high fiber content contributes to digestive regularity, promoting gut health and potentially reducing the risk of constipation. Furthermore, green peas are a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin K, vitamin C, and folate, all essential for various bodily functions.
Canned green peas offer a convenient source of vitamins and fiber, though sodium content can vary between brands. A comparison of their nutritional profile to other healthy options, such as those detailed in the natural pb nutrition facts guide, highlights the importance of balanced eating. Ultimately, canned green peas contribute valuable nutrients to a varied diet, especially when considering overall dietary intake.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the potential downsides associated with canned varieties.
Sodium Content in Canned Green Peas
The canning process often involves adding salt, which significantly increases the sodium content of the peas compared to their fresh or frozen counterparts. High sodium intake is linked to several health problems, including high blood pressure and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, individuals watching their sodium intake, particularly those with hypertension, should be mindful of the amount of canned peas they consume and opt for low-sodium varieties whenever possible.
Reading nutrition labels carefully and choosing brands with lower sodium content is crucial.
Impact of Canned Green Peas on Diabetes and Heart Health
The glycemic index (GI) of canned green peas is relatively moderate. While they can contribute to blood sugar levels, their fiber content can help slow down glucose absorption, minimizing the potential for sharp spikes in blood sugar. This makes them a potentially suitable addition to the diets of individuals with diabetes, although portion control remains important. For heart health, the fiber and nutrient content of green peas can be beneficial, contributing to lowering cholesterol levels and promoting cardiovascular well-being.
However, the high sodium content in some canned varieties can offset these benefits, highlighting the importance of choosing low-sodium options.
- Diabetes: Moderate glycemic index, fiber helps slow glucose absorption. Portion control is key.
- Heart Health: Fiber and nutrients can lower cholesterol. High sodium content in some brands can be detrimental. Choose low-sodium options.
Processing Methods and Nutritional Value, Canned green peas nutrition facts
The canning process, while convenient, can affect the nutritional content of green peas. While some nutrients remain stable, others, such as vitamin C, may be reduced during processing and storage. Compared to fresh or frozen peas, canned peas may have slightly lower levels of certain vitamins and antioxidants. However, the convenience factor often outweighs this slight reduction for many consumers.
The impact on overall nutritional value is relatively minor, especially when considering canned peas as part of a varied and balanced diet.
Canned Green Peas in a Balanced Diet: Canned Green Peas Nutrition Facts
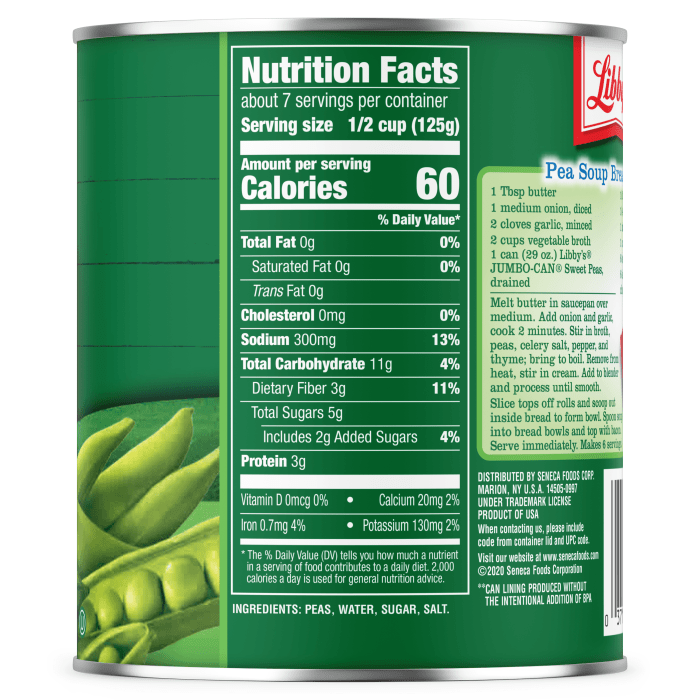
Canned green peas, often overlooked as a culinary staple, offer a surprisingly versatile and nutritious addition to a balanced diet. Their affordability and long shelf life make them a convenient choice for busy individuals and families seeking to incorporate more vegetables into their meals. Beyond simple side dishes, canned peas can elevate the flavor and nutritional profile of a wide range of recipes, from soups and stews to pasta sauces and salads.Canned green peas seamlessly integrate into a healthy eating plan by providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Their compact size allows for easy incorporation into various dishes without overwhelming other ingredients. Their mild flavor complements both savory and sweet preparations, making them a truly adaptable ingredient. A balanced diet emphasizes variety, and canned green peas contribute to this diversity by offering a readily available source of plant-based nutrients.
Recipe Examples and Preparation Times
The following table showcases three diverse recipes highlighting the versatility of canned green peas. These examples demonstrate how easily canned peas can be incorporated into different meal types, adding both flavor and nutritional value. Preparation times are estimates and may vary based on individual cooking skills and kitchen efficiency.
| Recipe Name | Serving Size | Preparation Time | Ingredients (highlights) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creamy Pea and Mint Pasta | 4 servings | 20 minutes | Pasta, canned peas, fresh mint, cream cheese, Parmesan cheese, garlic |
| Chicken and Pea Curry | 6 servings | 35 minutes | Chicken breast, canned peas, coconut milk, curry powder, onions, ginger |
| Simple Pea and Potato Salad | 6 servings | 15 minutes | Potatoes, canned peas, mayonnaise, celery, red onion, Dijon mustard |
Nutritional Comparison with Other Vegetables
While fresh vegetables are generally preferred for their higher nutrient density, canned green peas still offer significant nutritional benefits when compared to other commonly used vegetables. While the canning process may reduce some vitamin content, particularly heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C, canned peas retain a considerable amount of essential nutrients. For instance, canned peas are a good source of vitamin K, fiber, and folate, comparable to or exceeding the nutrient profile of some other canned or frozen vegetables.
The specific nutritional composition can vary depending on the brand and canning process, so it’s advisable to check individual product labels. However, overall, canned green peas provide a valuable contribution to a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals. Consider that other common vegetables, like canned corn or carrots, also offer unique nutritional profiles, and a balanced diet ideally includes a variety of vegetables to maximize nutrient intake.
Essential FAQs
Are canned green peas as nutritious as fresh peas?
While some nutrients are lost during the canning process, canned peas still retain a significant amount of vitamins and minerals. The nutritional differences aren’t always dramatic, and canned peas offer a convenient and affordable way to incorporate these nutrients into your diet.
How much sodium is in canned green peas?
Sodium content varies significantly between brands. Always check the nutrition label and choose low-sodium options whenever possible. Rinsing the peas before consumption can also help reduce sodium levels.
Can I use canned peas in recipes that call for fresh peas?
Absolutely! Canned peas are a great substitute in many recipes. Just be aware that their texture might be slightly different, and you might need to adjust cooking times accordingly.
Are there any specific health conditions where I should limit canned pea consumption?
Individuals with kidney disease may need to monitor their potassium intake, as canned peas are a good source of potassium. Consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.



