Ideal Planting Time for Pea Seeds

Source: gardeningknowhow.com
When to plant pea seeds – The success of your pea crop hinges significantly on planting at the optimal time. This depends primarily on your local climate, specifically your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone, and the microclimate of your garden. Understanding these factors allows for maximizing germination and yield.
Ideal Planting Times Based on Climate, When to plant pea seeds

Source: jungseed.com
The following table provides a general guideline for ideal planting times based on USDA Plant Hardiness Zones. Remember that microclimates can significantly influence these times.
| Zone | Planting Time (Spring) | Planting Time (Fall) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-4 | Late April – Early May | September – October (in milder areas) | Consider late spring frost dates. Fall planting may not be successful in all areas. |
| 5-6 | Mid-April – Late May | Late September – Early October | Monitor soil temperature; plant when consistently above 50°F (10°C). |
| 7-8 | March – April | October – November (in warmer areas) | Early planting allows for a longer growing season. |
| 9-10 | February – March | November – December (in some areas) | Consider potential for heat stress during summer months. |
Microclimates, such as areas with better sun exposure or those sheltered from wind, can experience warmer temperatures, allowing for earlier planting. Conversely, cooler, shadier areas may require later planting. Soil temperature plays a crucial role; peas germinate best in soil temperatures between 40-70°F (4-21°C).
The following flowchart illustrates the decision-making process for determining the best planting time.
(Flowchart description: The flowchart would begin with “Determine your USDA Plant Hardiness Zone.” This would branch to “Check average last frost date” and “Check average first frost date”. Each of these would branch to “Check soil temperature” which would lead to “Plant peas!” or “Wait for warmer temperatures”. The flowchart would also include considerations for microclimates and potential for fall planting).
Soil Preparation and Seed Selection
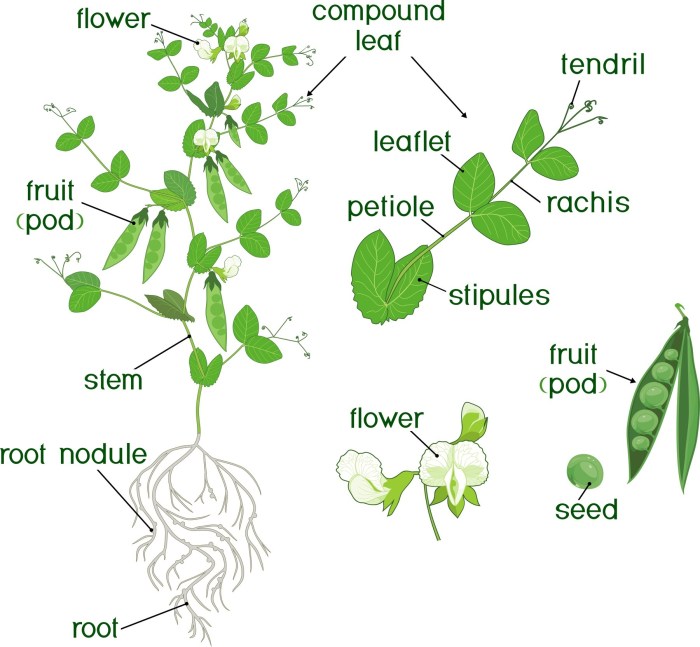
Source: albertapulse.com
Proper soil preparation and seed selection are crucial for a successful pea harvest. High-quality seeds planted in well-prepared soil will result in better germination and stronger plants.
- Test your soil to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Amend as needed to achieve a slightly acidic pH (6.0-6.8) and add compost for improved drainage and fertility.
- Loosen the soil to a depth of 12-18 inches to allow for good root development.
- Remove any rocks, weeds, and debris from the planting area.
- Water the soil thoroughly before planting.
Pea seed varieties differ in maturity times and climate suitability. Selecting high-quality seeds ensures optimal germination rates. Look for plump, firm seeds free of blemishes.
| Variety | Maturity Time | Climate Suitability | Seed Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Peas (e.g., ‘Little Marvel’) | 50-60 days | Cool climates | Small, round, green |
| Mid-Season Peas (e.g., ‘Oregon Sugar Pod II’) | 60-70 days | Moderate climates | Medium size, round, green |
| Late Peas (e.g., ‘Lincoln’) | 70-80 days | Warm climates | Large, round, green |
Planting Methods and Techniques
Several planting methods offer different advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right method depends on your experience and available resources.
- Direct Sowing: This involves planting seeds directly into the prepared soil. It’s the most common method, simple and cost-effective, but susceptible to weather conditions and pests.
- Starting Indoors: Starting seeds indoors provides a head start, increasing the chances of a successful harvest, but requires more effort and resources.
- Succession Planting: This involves planting seeds at intervals throughout the growing season, ensuring a continuous harvest. This method requires more planning and monitoring.
For direct sowing, plant seeds 1-2 inches deep, 2-4 inches apart, and in rows 18-24 inches apart. For starting indoors, use seed trays with a suitable potting mix, keeping the soil consistently moist.
Succession planting extends the harvest period by planting new seeds every 2-3 weeks, depending on the variety.
Post-Planting Care and Maintenance
Consistent care is crucial for healthy pea plants and a bountiful harvest. Regular watering, mulching, and pest control are key aspects of post-planting care.
| Watering Method | Effectiveness | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | High | Efficient water use, reduces weed growth | Higher initial cost |
| Overhead Watering | Moderate | Simple, inexpensive | Can lead to fungal diseases, water wastage |
Mulching helps retain soil moisture and suppress weeds. Common pea pests include aphids and pea weevils. Preventative measures include crop rotation, using pest-resistant varieties, and monitoring for infestations.
(Image description: A picture showing aphids clustered on a pea plant leaf. Another image showing pea weevils on a pea pod. A third image illustrating healthy pea plants with a layer of mulch around their base.)
(Post-planting care schedule: A table outlining weekly tasks, including watering frequency, weeding, pest control checks, and harvesting periods throughout the growing season).
Harvesting and Storage
Harvest peas when the pods are plump and full, but before they become overly large or hard. Proper harvesting and storage techniques ensure the best flavor and nutritional value.
Harvesting involves carefully snapping or pulling the pods from the vines. Different preservation methods include freezing, canning, and drying. Freezing preserves flavor and texture well, while canning offers a longer shelf life. Drying is suitable for long-term storage, but may affect the texture.
(Visual guide description: A step-by-step visual guide demonstrating the proper techniques for shelling peas, showing how to remove the pods from the vines and then open the pods to extract the peas. The guide would also include images illustrating the proper way to prepare peas for different storage methods).
FAQ Compilation: When To Plant Pea Seeds
How deep should I plant pea seeds?
Plant pea seeds about 1-2 inches deep.
How far apart should I space pea plants?
Spacing depends on the variety, but generally, allow 2-4 inches between plants and 18-36 inches between rows.
What should I do if my pea plants are showing signs of disease?
Remove affected plants immediately, improve air circulation, and consider using appropriate fungicides.
Can I save pea seeds from my harvest for next year?
The ideal time to plant pea seeds is typically in the fall or early spring, depending on your climate. Understanding soil temperature is key, much like knowing the best time to plant other seeds, such as when determining when to plant grass seed in north texas , which also hinges on optimal soil conditions. Therefore, before planting peas, check your local weather forecasts for suitable temperatures to ensure successful germination and growth.
Yes, but ensure the seeds are from healthy, open-pollinated varieties. Properly dry and store the seeds in a cool, dry place.
When is the best time to harvest peas for freezing?
Harvest peas when they are young, tender, and plump, but before they become overly large or hard.



