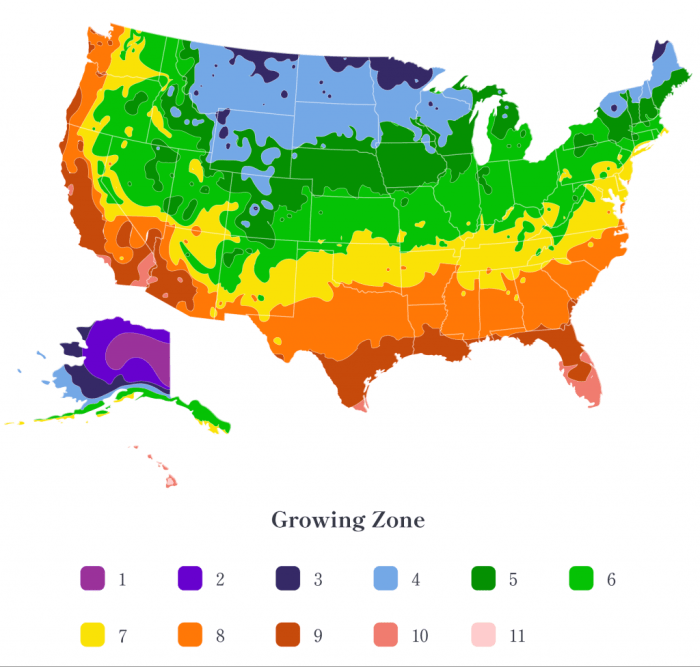
Understanding USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 8
When to plant poppy seeds zone 8 – USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 8 encompasses a wide range of climates, influencing the optimal planting times for poppy seeds. Understanding these variations is crucial for successful cultivation.
Zone 8 Climate Characteristics and Their Impact on Poppies
Zone 8 experiences mild winters with average minimum temperatures ranging from 10°F to 20°F (-12°C to -7°C). Summers are typically warm and humid, with temperatures frequently exceeding 80°F (27°C). These temperature fluctuations significantly affect poppy germination and growth. Poppies generally require cool soil temperatures for optimal germination, while excessive heat can hinder seedling establishment. Rainfall patterns also vary within Zone 8, impacting soil moisture levels crucial for poppy development.
Consistent moisture is needed during germination and early growth, but mature poppies tolerate some drought.
Microclimate Variations Within Zone 8
Significant microclimate variations exist within Zone 8. Coastal areas tend to have milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland regions. Elevated areas may experience cooler temperatures and more frost, while sheltered locations can enjoy warmer conditions. These microclimatic differences directly impact the ideal planting time for poppies. Coastal areas might allow for slightly earlier planting in spring or later planting in fall compared to inland locations.
Poppy Seed Varieties Suitable for Zone 8
Source: trees.com
Several poppy varieties thrive in Zone 8, each with unique characteristics influencing planting strategies. Choosing the right variety ensures optimal bloom times and plant health.
Poppy Variety Comparison
| Variety | Bloom Time | Soil Conditions | Sunlight | Mature Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oriental Poppy (Papaver orientale) | Late Spring/Early Summer | Well-drained, slightly alkaline soil | Full sun | 2-3 feet tall |
| California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica) | Spring/Summer | Well-drained, sandy loam | Full sun | 1-2 feet tall |
| Iceland Poppy (Papaver nudicaule) | Spring/Summer | Well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soil | Full sun to partial shade | 1-2 feet tall |
| Shirley Poppy (Papaver rhoeas) | Late Spring/Early Summer | Well-drained soil, tolerates various pH levels | Full sun | 1-2 feet tall |
Sunlight Exposure and Mature Plant Size
Oriental poppies prefer full sun and reach a considerable height, requiring adequate spacing. California poppies also thrive in full sun, but are more compact. Iceland poppies tolerate partial shade, offering flexibility in garden placement. Shirley poppies are adaptable to full sun and are relatively short, making them suitable for borders or containers.
For optimal germination, planting poppy seeds in Zone 8 ideally occurs in the fall, allowing them to benefit from the cooler temperatures. This timing contrasts with the best time to sow herbs like oregano; for information on that, check out this guide on when to plant oregano seeds. Returning to poppies, spring sowing is also possible, but fall planting generally yields better results in Zone 8.
Optimal Planting Times for Poppy Seeds in Zone 8: When To Plant Poppy Seeds Zone 8
The ideal time to plant poppy seeds in Zone 8 depends on several factors, including the specific variety and whether you’re planting in spring or fall. Each approach offers advantages and disadvantages.
Spring and Fall Planting: Advantages and Disadvantages, When to plant poppy seeds zone 8
Spring planting (March-April) allows poppies to take advantage of the warming soil temperatures and longer days, leading to robust growth and abundant blooms. However, spring planting can be susceptible to late frosts. Fall planting (September-October) offers the advantage of cooler temperatures, ideal for germination, and established seedlings benefit from the winter moisture. However, fall planting may result in delayed blooming the following spring.
Soil Preparation for Spring and Fall Planting
For both spring and fall planting, prepare the soil by removing weeds, rocks, and debris. Loosen the soil to a depth of 6-8 inches to improve drainage and aeration. Incorporate compost or other organic matter to enhance soil fertility and water retention. For fall planting, ensure the soil is adequately moist but not waterlogged.
Sowing Poppy Seeds: Methods and Techniques
Sowing poppy seeds directly into the ground is the most common method. Alternatively, starting seeds indoors offers more control over germination and early growth, though transplanting requires care.
Direct Sowing of Poppy Seeds
1. Prepare the soil as described above.
2. Broadcast poppy seeds evenly over the prepared area.
3.
Lightly rake the seeds into the soil, covering them with about ⅛ inch of soil.
4. Gently water the area, avoiding dislodging the seeds.
5. Thin seedlings to the desired spacing once they have developed several true leaves.
Thinning Poppy Seedlings
Thinning helps prevent overcrowding and promotes better air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Carefully remove excess seedlings, leaving adequate space between plants based on the mature size of the chosen variety.
Starting Poppies Indoors and Transplanting
- Sow seeds in seed trays or small pots filled with seed-starting mix.
- Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy.
- Provide adequate light, either using grow lights or a sunny windowsill.
- Once seedlings have developed several true leaves, harden them off gradually by placing them outdoors for short periods.
- Transplant seedlings outdoors after the last expected frost, spacing them appropriately.
Post-Planting Care for Poppies in Zone 8
Consistent watering, proper drainage, and pest and disease management are essential for healthy poppy cultivation in Zone 8.
Watering Requirements
Water regularly during germination and early growth to maintain consistent soil moisture. Once established, poppies tolerate some drought, but consistent watering during prolonged dry spells is beneficial, especially during blooming. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Soil Drainage and Pest/Disease Control
Source: removeandreplace.com
Well-drained soil is crucial to prevent root rot. Poppies are relatively pest-resistant, but aphids and slugs can be problematic. Regular monitoring and appropriate pest control measures, such as handpicking or using organic insecticides, are recommended. Fungal diseases can occur in wet conditions; ensure good air circulation to minimize risk.
Illustrative Examples of Successful Poppy Cultivation in Zone 8
Successful and less successful poppy cultivation scenarios highlight the importance of proper techniques and environmental considerations.
Example of a Thriving Poppy Patch
Imagine a vibrant patch of Oriental poppies in a sunny corner of a Zone 8 garden. The rich, well-drained soil, amended with compost, is slightly alkaline. The poppies, planted in fall, stand tall, their scarlet blooms a breathtaking contrast against the deep green foliage. The air is filled with the subtle, earthy fragrance of the blossoms. The plants, spaced appropriately, receive ample sunlight and air circulation, resulting in healthy growth and minimal pest issues.
Regular, but not excessive, watering maintains optimal soil moisture.
Example of a Less Successful Poppy Planting
In contrast, consider a less successful planting of California poppies in a poorly drained, clay soil area with insufficient sunlight. The seeds, sown in spring, struggled to germinate due to compacted soil and cold, wet conditions. Overwatering further exacerbated the problem, leading to damping-off disease and the loss of many seedlings. The remaining plants were stunted and produced few blooms.
This illustrates the importance of proper site selection, soil preparation, and appropriate watering techniques.
General Inquiries
What type of soil is best for poppies in Zone 8?
Poppies thrive in well-drained, slightly alkaline soil. Amend heavy clay soils with compost to improve drainage.
How deep should I plant poppy seeds?
Poppy seeds are tiny; barely cover them with soil. Light soil contact is sufficient for germination.
Can I start poppy seeds indoors in Zone 8?
While possible, direct sowing is generally preferred for poppies. Starting indoors can be challenging due to their delicate roots.
What should I do if my poppies are not blooming?
Insufficient sunlight, poor drainage, or inadequate watering can all inhibit blooming. Review your planting conditions and adjust as needed.



